A signing bonus is a one-time lump sum payment given to an athlete at the time of signing a new contract.
Signing bonuses are typically included in rookie deals, free agent signings, and extensions.
Unlike base salary, which is paid weekly or over the course of a season, signing bonuses are typically guaranteed and paid upfront or within the first contract year.
However the signing bonus is accounted for, taxed, and applied to the salary cap, depends on the sport.
Teams and leagues use signing bonuses to attract talent, manipulate the cap, and secure long term commitment.
For players, they often view it as the safest form of money they’ll receive outside of guarantees.
How Signing Bonuses Work In Different Leagues
🎓NCAA / NIL Athletes
Signing bonuses don’t formally exist in the NCAA because athletes don’t sign salary contracts, they sign scholarship agreements and earn NIL income from third parties.
However, NIL has created bonus-like mechanisms that function similarly:
- Lump-sum NIL payouts at signing
- Upfront multi-year collective deals
- Booster-backed “commitment bonuses”
- Transfer-portal incentives
- Retention packages
These are not technically signing bonuses in the contract-law sense, but:
- Financially: They serve the same purpose, upfront cash to secure commitment.
- Legally: They are NIL compensation, not salary, not consideration for performance.
- Strategically: They influence recruiting, retention, and transfer decisions.
NCAA NIL moved amateurism closer to professional contracting, just without salary caps or true employment contracts (yet).
Use Cases
- 5-star QB receives a $500K NIL lump sum upon committing
- Collective offers a guaranteed 1-year NIL package for a transfer portal player
- Donor-backed NIL retention deals prevent departures to rival schools
Example
A top WR may choose a school offering a $1.2 million NIL package, where $400–600K is delivered upfront upon signing the NIL contract. This is not a signing bonus on paper, but is financially identical.
🏈NFL
The signing bonus is most common in the National Football League (NFL). The league also allows the most room for strategic use and cap flexibility.
Use Cases
- Paid to player immediately, but prorated up to 5 years for cap purposes.
- Used in rookie deals, extensions, and veteran restructures.
- Key for keeping stars while manipulating the salary cap.
Example
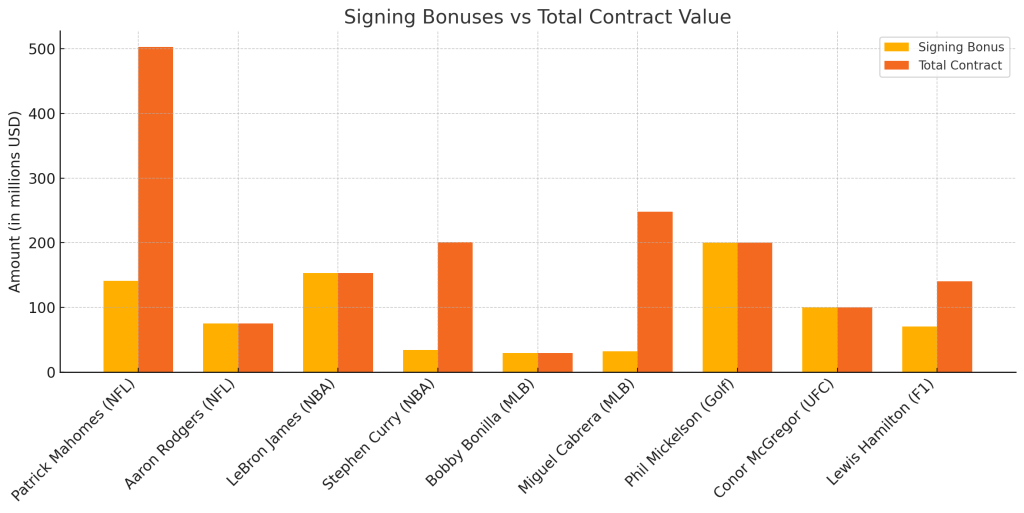
Dak Prescott’s (Dallas Cowboys) $80 million signing bonus was paid instantly, but only hit $20M/year on the cap due to proration.
🏀NBA
The signing bonus in the NBA is used occasionally, however its use is less flexible than in the NFL.
Use Cases
- Bonuses may appear in rookie deals, or unique incentives.
- The NBA uses a soft cap, making it so other tools take priority.
(exceptions, guarantees, and others). - Bonus is not prorated and hits cap when paid.
Example
Zion Williamson (New Orleans Pelicans) received ~$24 million in bonuses on his rookie extension.
⚾MLB
The use of the signing bonus in the MLB is most common in draft and international deals.
Use Cases
- No salary cap = no proration games.
- Treated as guaranteed cash.
- Players like Paul Skenes and Shohei Ohtani receive multi-million-dollar signing bonuses early.
Example
Paul Skenes received a $9.2 million signing bonus when he was selected to the Pittsburgh Pirates as the No. 1 overall pick in 2023 MLB draft.
🏒NHL
Signing bonuses in the NHL are often part of front-loaded veteran deals.
Use Cases
- Useful for lockout protection, since bonuses are paid even if the season is suspended.
- Not prorated, but can impact how long-term value is measured.
- Seen as a loyalty / protection mechanism more than a financial trick.
Example
Auston Matthews (Maple Leafs) received $60.5 million of his 5-year deal structured in his signing bonus.
⚽MLS & International Soccer
Signing bonuses in soccer function very differently depending on the league. In MLS, bonuses are structured more like the NFL/NBA, upfront money paid at signing, guaranteed, and often used to attract top Designated Player talent without blowing up the salary cap.
In international soccer, especially in Europe, signing bonuses are massive.
They’re Used To
- Win bidding wars for star players.
- Compensate free agents (Bosman transfers).
- Secure long-term contracts.
- Offset lower weekly wages in certain clubs.
- Incentivize players to move to smaller leagues.
Use Cases
MLS
- Used heavily for Designated Players (Beckham Rule).
- Helps teams stay cap-compliant.
- Paid in addition to the player’s guaranteed salary.
- Often tied to marketing value, not just on-field talent.
International
- Superstar free transfers (Messi to PSG, Mbappé rumors, etc.)
- New contract renewals.
- Loyalty bonuses for staying at a club.
- Youth prospects signing their first pro deal.
Signing bonuses in global soccer are often higher than the annual salary itself, because clubs don’t deal with luxury tax, hard caps, or rookie scales like U.S. leagues.
MLS Example
In MLS, Lorenzo Insigne received a huge signing bonus to join Toronto FC even though his cap hit was artificially reduced because he was a Designated Player.
International Example
When Lionel Messi joined PSG in 2021, he earned:
- A massive signing bonus (reportedly over $25M)
- Loyalty bonuses
- Endorsements tied to the contract
🥊UFC / Combat Sports
Because the UFC and most combat sports are individuals competing, the signing bonus does exist in fighter contracts, but are typically less structured than in team leagues.
Use Cases
- Fighters may receive signing bonuses for joining a promotion or when they are in the process of extending their fight contracts.
- Usually paid up front and outside of the official “fight purse.”
- Not common, but can be used to land top-tier talent from other organizations (e.g., PFL, Bellator).
Example
Michael Chandler received a signing bonus when he decided to leave the Bellator for the octagons in the UFC.
⛳Golf / Individual Sports
Similar to combat sports, sports like golf and tennis are often individuals competing amongst themselves.
However in golf, tennis and other individual sports, signing bonuses are rare unless part of a sponsorship, team event, or LIV/PGA Tour contract.
Use Cases
- LIV Golf introduced massive signing bonuses.
(e.g., Phil Mickelson’s reported $200M). - PGA Tour traditionally does not offer bonuses, but certain NIL-style sponsorships have begun to include them now.
Example
Brooks Koepka, Bryson DeChambeau and Dustin Johnson were all offered and accepted 9-figure LIV deals, which included bonuses.
🏎️Racing / NASCAR / F1
Signing bonuses have several names, but again it is the immediate payment of promised funds at the time of signing a new contract.
The use of the signing bonus is more common in F1, where teams give bonuses for joining or renewing.
Use Cases
- Sometimes paired with performance clauses (podiums, wins, etc.).
- NASCAR/F1 use win/share-based payouts more than signing bonuses, however there are clauses where racers get paid a sum on signing.
Example
Max Verstappen (Red Bull) has made a fortune, which included $50M+ in bonus earnings over his championship years.
Why Signing Bonuses Matter
Players see signing bonuses as one the safest parts of their contract outside of guarantees, as they are usually paid no matter what.
Unless, there are certain clauses in place that void payments due to external factors. Teams and companies use it to show trust in their athletes, sweeten the pot, and in leagues that allow it, spread out and manipulate their cap hits.
From a financial angle:
It affects tax strategy, guarantee structure, and the organizations ability to maintain long-term value.
They are able to pay top talent to maximum deals, while also maintain the ability to sign a capable squad around superstars and high value players.
Graphic
🔗Related Terms
🔗Next Reads
- How NFL Signing Bonuses Are Structured
- Five Signing Bonuses That Changed the Landscape of the NFL
- Top Largest NFL Contract Values 2015-2025
- Top 5 Longest NHL Contracts In History
- Top 7 Largest Total Value Contracts In Pro Sports History
“Now faith is confidence in what we hope for and assurance about what we do not see.”
– Hebrews 11:1